

- Home
-
Product
Product
-
Connect
seamlessly any application, device or data
source
-
Data Link &
Integration...
-
Data Link & Integration
We support connecting to the following 4 types of data sources to provide basic data for subsequent data processing and integration...
-
-
Analyze Delivery &
Messaging
-
Analyze Delivery & Messaging
Secure, reliable, real-time data distribution is a crucial part of your digital infrastructure. We can auto delivery analysis and Messaging...
-
-
Analyze Store & Sharing
-
Analyze Store & Sharing
A personalized portal with thousands of people, seamless communication between template users and authors, and a growth platform for business analysts...
-
-
Data Link &
Integration...
-
Unify
data intelligently for better access, trust,
and
control
-
Data Collection
-
Data Collection
Through the data collection function, enrich the data in the platform to meet the subsequent analysis needs...
-
-
Data Processing
-
Data Processing
Data processing refers to the cleaning, conversion, and loading of data before data analysis...
-
-
Cross-Database
Integration
-
Cross-Database Integration
Enterprise data is stored in different servers or even different types of databases. When users query data in a wide range and are not limited to one database...
-
-
Data Control & Query
-
Data Control & Query
Synapse supports the access of rich data sources, but generally it is not possible to directly use the accessed service library for data analysis...
-
-
Massively Parallel
Processing DW
-
Massively Parallel Processing DW
With the mature application of distributed and parallel technology, the MPP engine database has gradually shown strong high-throughput and low-latency computing capabilities...
-
-
Data Collection
-
Predict
confidently with real-time data-driven
intelligence
-
Analytics
-
Analytics
From data preparation, style design, data calculation, data visualization to interactive logic, sharing and publishing of report development...
-
-
Machine Learning
-
Machine Learning
In recent years, data mining has attracted great attention in the industry. The main reason is that there is a large amount of data...
-
-
Natural Language
Analysis
-
Natural Language Analysis
With the widespread popularity of the Internet, the social demand for language information processing is increasing...
-
-
Analytics
-
Connect
seamlessly any application, device or data
source
-
Solution
Solution
-
Industry Solution
Automotive, High Tech, Industrial Machinery and Components, Consumer Products, Fashion, Life Sciences, Retail, Whosale Distribution
-
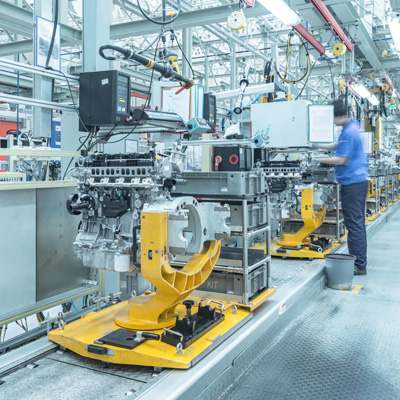
Automotive
-
Automotive
With the competition in the automotive landscape, the stakes are often high. Digital transformation is a key strategy...
-
-
High Tech
-
High Tech
You can calculate your RGR over many periods, such as month over month, quarter over quarter or year over year...
-
-
Industrial Machinery and
Components
-
Industrial Machinery and Components
Companies in Industrial Machinery and Components Industries are facing a demand for high levels of automation and coping...
-
-
Consumer Products
-
Consumer Products
A consumer products KPI or metric is a measurable value that helps to monitor and accomplish pre-defined organizational goals...
-
-
Fashion
-
Fashion
Store owners usually check revenue, profit, number of visitors, average shopping basket... sometimes it is difficult to say what caused the increase in results...
-
-
Life Sciences
-
Life Sciences
Life Sciences sector covers a large variety of players. A number of parameters come into play when developing a new product...
-
-
Retail
-
Retail
While running a retail business, it’s easy to lose sight of goals and performance. Business owners have to keep track of a number of aspects...
-
-
Wholesale Distribution
-
Wholesale Distribution
In Wholesale, as in any business, keeping a keen eye on the past, current and future financial performance of the business is key to continued growth...
-
-
Automotive
-
Business Solution
Manufacturing, Sales Marketing, Finance, HR
-
Manufacturing
-
Manufacturing
How can IT help a manufacturing company more accurately monitor, control, and predict cost associated with factory operations spread around the world...
-
-
Sales Marketing
-
Sales Marketing
Whatever offers you develop, you first need to understand your customers before designing appropriate promotions to fit their current and future needs....
-
-
Finance
-
Finance
Every company wants to manage their costs efficiently and effectively. That task can be particularly challenging...
-
-
HR
-
HR
If you’re an HR manager and your company has an aggressive growth strategy, you need to retain your high performing employees...
-
-
Manufacturing
-
Industry Solution
Automotive, High Tech, Industrial Machinery and Components, Consumer Products, Fashion, Life Sciences, Retail, Whosale Distribution
- Partner
- About
 Contact Us On+1 (650) 600 9071
Contact Us On+1 (650) 600 9071






















 En
En